Solder Mask may not be an interesting topic in electronic circuit manufacturing, but it is an extremely important topic. Without this coating, your printed circuit board may suffer from short circuits, corrosion, and many other problems that affect the quality and lifespan of the board. Therefore, if you want to have high-quality, reliable and durable electronic products, you need to grasp the necessary knowledge about coatings from the purpose of use and types of coatings to their applications in circuit board design. In this article, we will bring you all the basic knowledge about coatings on the surface of PCB circuit boards. Hopefully, the knowledge we share in this article will be useful and help you achieve better results in your design projects.

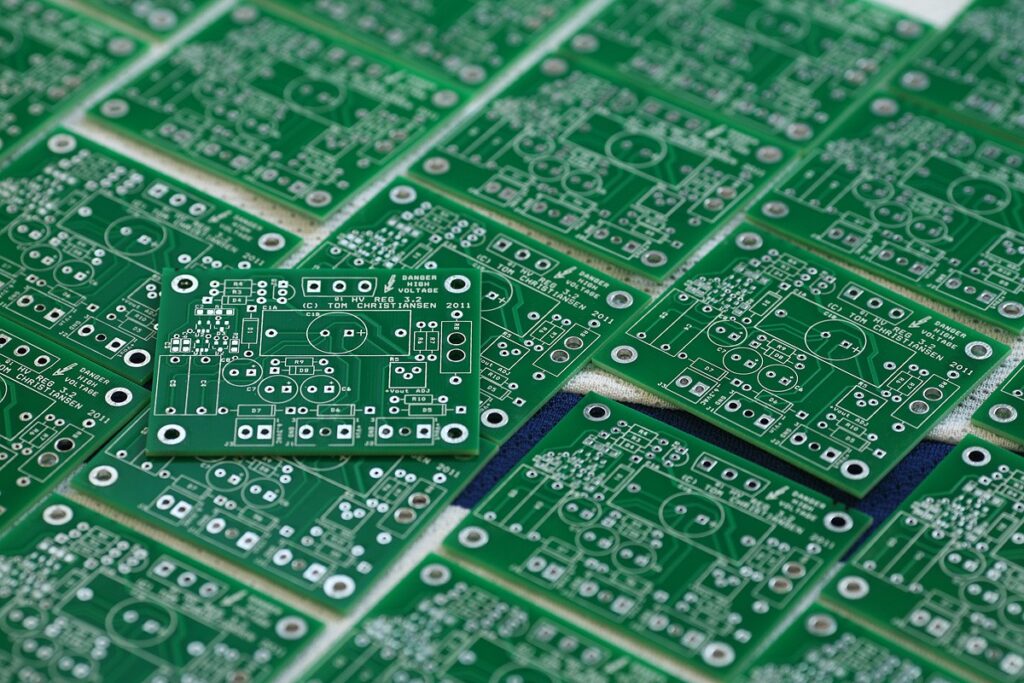
Figure 1. Solder Mask coating on the surface of the PCB circuit board
1. Uses of Solder Mask coating
Before going into the detailed discussion of Solder Mask, let’s talk about its uses and benefits. Solder Mask is a thin layer of polymer material coated on the surface of the circuit board to protect the copper circuit from environmental factors such as dust, humid air, heat, and against oxidation. The Solder Mask layer gives the circuit board a contrast between the components and the Silk Screen character layer, helping to simplify the inspection and repair process. In addition, Solder Mask also makes it easier to solder components to the circuit board by preventing solder from flowing to unwanted areas, helping to avoid short circuits, improving the performance, quality and reliability of the circuit board. Some of the main functions of the Solder Mask layer can be mentioned as:
- Protect the circuit board from environmental impacts. Protect circuit lines from oxidation and dirt that can easily lead to reduced transmission capacity, signal attenuation and interference…
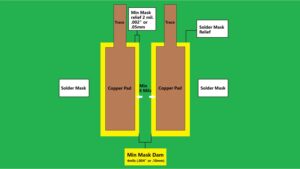
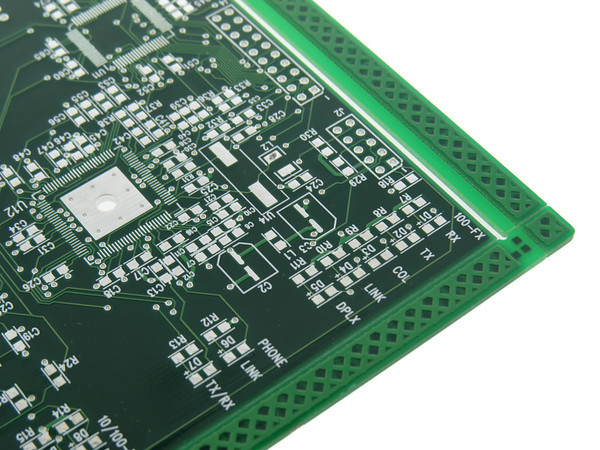
Figure 2. The coating acts as a separator between the two soldering pads.
- Reduces short circuits, short circuits, and limits soldering errors (bridging solder joints, etc.). When solder is melted at the soldering point, it always tends to flow to areas with the highest heat transfer capacity, thereby easily creating unwanted connections between different parts of the printed circuit board. By using Solder Mask to delineate areas where solder can and cannot flow, you can limit unwanted connections and ensure accurate soldering of the printed circuit board.
- Increase the contrast with the Silk Screen text layer as well as the components on the PCB. Using high-contrast coating colors such as green, black, etc. makes it easy to identify components as well as the symbols of the location and direction of the components on the text layer on the circuit board, which is especially important for circuit boards with high complexity and high component density. This can minimize errors during the welding process as well as save time and effort in detecting errors and repairing circuit boards.
2. Types of Solder Mask
Currently, there are three main types of coatings on the market, including:
- Liquid Photoimageable Solder Mask (LPSM). This is quite popular due to its flexibility, ease of use and low cost. LPSM is coated on the PCB surface in liquid form and then solidified under the influence of ultraviolet (UV) rays. Areas that do not need to be coated, such as solder pads, will be protected by a photoresist that blocks UV rays, and the unsolidified coating in these areas will be washed off later. LPSM can be used for both 1-layer and 2-layer circuits and can be cured by UV or Heat.
- Dry Film Solder Mask (DFSM). DFSM is a type of paint in the form of a dry film that is applied to the PCB surface under the influence of heat and pressure. DFSM is often used in industrial PCB manufacturing plants to produce complex circuit boards with high component density that require high precision, which LPSM liquid coating cannot meet. DFSM is also used when processing multi-layer circuits to coat the surface of the circuit board before drilling Via holes. However, film coating is more expensive and time-consuming, requiring specialized equipment and expertise to perform and is often used in modern PCB manufacturing plants.
- Thermally Cured Solder Mask (TCSM). This is a liquid coating that is solidified under the effect of temperature and pressure after being coated on the surface of the printed circuit board. TCSM is often used for special applications that require high temperatures, or can be affected by chemicals that LPSM and DFSM coatings cannot meet. This type of coating technology has a higher chemical resistance than other types of coatings, so it is often used in harsh or corrosive environments. TCSM coatings are often quite expensive and the production of circuits using this type of coating is also time-consuming and requires higher equipment and techniques than conventional coatings.
3. PCB Surface Coating Process
Usually, the PCB surface coating process usually includes three main steps including:
- Surface cleaning. This step includes cleaning and preparing the surface of the printed circuit board to ensure the best adhesion and solidification. Specific tasks include removing grease, chemicals; scrubbing, etching, washing… depending on the nature and condition of the Solder Mask and the printed circuit board.
- Printing. Liquid Solder Mask will be spread evenly over the entire surface, while film Solder Mask will be placed and pressed tightly onto the printed circuit board surface.
- Solidification: The Solder Mask will be solidified under the effect of ultraviolet rays, high temperatures, or a combination of both. In some cases, pressing is required to complete the solidification process. The solidification process depends on the type of mask and the manufacturer, and may require different levels of temperature, time, and pressure.
4. Factors to consider when choosing a coating type
Choosing the right coating often depends on the technical requirements and constraints of the circuit board. But in general, there are some factors you need to consider such as:
- Compatibility with the type of circuit board material. The coating used needs to be compatible with the type of PCB material to ensure adhesion, solidification and efficiency.
- Coating color. The coating used should have many color options, ensuring contrast for easy processing and repair as well as meeting the aesthetic requirements of the circuit board.
- Heat resistance. The coating used needs to meet the requirements for heat resistance as well as the life of the circuit board without melting, cracking or peeling.
- Chemical resistance. The coating needs to meet the requirements for chemical resistance and corrosion resistance of the circuit board without reducing the performance of the circuit board.
5. Some common problems with Solder Mask coating on circuit boards and solutions
Some common problems with coating when processing PCB circuits are:
- Hole or gaps appear on the surface of the solidified coating layer, exposing the circuit or solder pad. This error can occur due to many reasons such as the PCB surface is not cleaned enough, the solidification process is not up to standard, or there are impurities. To avoid this error, it is necessary to ensure that the PCB surface is thoroughly cleaned, the paint must be applied uniformly on the surface, and the solidification process must be carried out at the appropriate temperature and time as recommended by the manufacturer.

Figure 3. Pinholes on the PCB Surface
- Peeling of the coating or circuit. This peeling can cause short circuits or connection failures. Causes of peeling can be lack of adhesion to the PCB surface, inadequate solidification, or coating under improper temperature and pressure conditions. To prevent this, it is necessary to choose a coating that is adhesive and compatible with the material the circuit is being processed. Avoid processing the circuit under harsh conditions or with sudden changes in temperature or pressure.

Figure 4. Peeling on the surface of the circuit board
- Over-solidification is a phenomenon where the Solder Mask layer is over-solidified, leading to brittleness, cracking or shrinkage. Over-solidification can be caused by many reasons such as too high a solidification temperature, too long a UV exposure time. To prevent it, you need to follow the recommended solidification parameters for temperature, time, and pressure.
- Under-solidification is when the Solder Mask layer does not reach the required hardness, resulting in a soft, sticky, wet surface. Under-solidification can be caused by insufficient temperature or insufficient UV exposure time. To prevent it, you need to ensure the correct parameters for temperature, time, pressure, and check the quality and adhesion of the Solder Mask before moving on to the next step.
6. The influence of Solder Mask coating on PCB circuit design
The coating can affect PCB design in several aspects such as:
- Layout design: The coating can limit the space and width of the circuit lines and solder pads. When designing the layout of the circuit, you need to pay attention to the maximum and minimum gaps and widths of the coating, to ensure complete coverage and protection of the circuit lines and solder pads. You should also avoid placing components and Via holes too close together or too close to the corners of the board to avoid difficulties when coating.
- Wiring: The coating can affect the wiring process because it delimits the areas where the circuit lines or solder pads can connect or not. When wiring, you need to pay attention to the position and size of the gaps on the coating to ensure connections between the circuit lines and solder pads without causing short circuits or bridging when soldering the circuit. You also need to pay attention not to wire or place the solder pad too close to the edges of the board to avoid being affected when painting.
- Component placement: Coating can also affect the space limitations for placing components as well as the dimensions of the components. When arranging components on the circuit, pay attention to the size and shape of the openings on the coating layer to ensure that the components can be soldered to the surface without being misaligned during processing… Avoid placing components too close to the edge of the circuit to avoid difficulties when painting.
Conclusion
Coating is an extremely important step in the PCB manufacturing process. Without the right Solder Mask layer, your printed circuit board may not be protected from short circuits, bridging, corrosion or many other complex problems that take a lot of time and money to fix. In this article, we have introduced to you everything you need to know about Solder Mask, from its intended use as well as different types of coatings to its applications and applications in design. We hope you can gain a lot of useful knowledge and tips to help you make progress in designing printed circuit boards. Remember, Solder Mask is not just a cosmetic layer, it is a particularly important component in a high-quality and reliable printed circuit board. Therefore, if you invest time and effort to learn and master it, you will be able to enjoy many achievements in the future.
If you have any difficulties or questions related to PCB design or processing, please contact us here for support. Hatakey.com.vn Electronics Company specializes in providing services related to PCB boards such as ordering printed circuit boards with different sizes and colors, processing and assembling circuit boards, designing circuit layouts, ordering electronic components from many reputable distributors. We can meet all the necessary needs of customers. Thank you for taking the time to read this article!




 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt