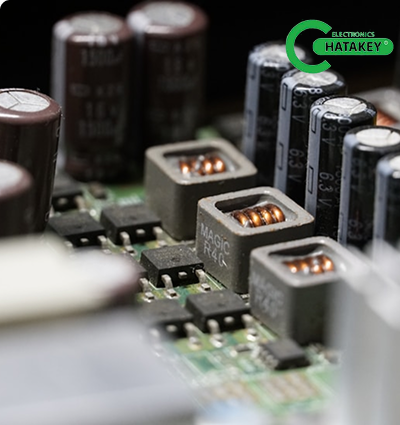
During the soldering process (PCBA), flux is used as a chemical agent to help solder components. However, if improperly cleaned, residual flux can affect the performance of the circuit over time. This effectively reduces the surface insulation resistance and affects the operation of the circuit. Additionally, an unclean PCB can accumulate external noise signals, further affecting the DC performance of the circuit. To address these issues, proper cleaning and drying are essential to ensure optimal board performance (Figure 1).

Figure 1: PCB Cleaning
I. Types of Soldering Fluxes and Cleaning Methods
1. Soldering Fluxes and Cleaning Methods:
- Water-soluble fluxes: These need to be rinsed with water (usually deionized water) after soldering to remove residue left over from the soldering process.
- Rosin-containing fluxes: These need to be cleaned with a solvent (such as isopropyl alcohol) to remove rosin and other residue.
- No-clean fluxes: These are designed to be cleaned after soldering because residue is usually not left behind and has minimal impact on electrical performance.

Figure 2: Some soldering fluxes
2. Main common PCB cleaning methods:
- Ultrasonic cleaning: This method is used to clean water-soluble soldering fluxes and rosin. It uses the cavitation effect created by ultrasonic vibration to remove residue.
- Alcohol brushing: This method is often used for small circuits or manual cleaning. Especially for cleaning rosin-based soldering fluxes (Figure 3).

Figure 3: Alcohol Cleaning Process
II. Ultrasonic Cleaning Method
Steps for Ultrasonic Cleaning:
- Check for any parts that are prone to peeling off or require special treatment. Then, select the appropriate cleaning solution based on the type of circuit contaminant.
- Place the ready PCB in the ultrasonic cleaning tank, ensuring that the PCB is completely submerged in the cleaning solution. Set the ultrasonic frequency according to the type of circuit contaminant and the complexity of the PCB.
- After cleaning, place the PCB in a deionized water wash tank to rinse several times to gradually reduce the amount of cleaning solution remaining. Follow this with a deionized water rinse, either by spraying or soaking, to further remove any remaining detergent and contaminants.
- After rinsing, use dry compressed air to blow off any water droplets from the PCB. Pay special attention to crevices, gaps, and underneath components where water is likely to accumulate. Then place the PCB in a hot air dryer to ensure complete drying.
- Check the PCB for cleaning residue, incomplete drying, or other contaminants.

Figure 4: Ultrasonic cleaning process
III. Conclusion
Maintaining the cleanliness of the PCB circuit is very important. This is to prevent circuit errors and improve the overall performance of the system. This is essential in the design and assembly process, ensuring that every detail meets high standards, thereby saving time and money. So we have completed learning about the PCB cleaning process. If you have any questions, you can contact our company HATAKEY Electronics to have our team of experienced technicians with many years of experience in the industry enthusiastically answer all your questions.
Hatakey.com.vn Electronics Company specializes in providing services related to PCB circuit boards such as ordering printed circuit boards with many different sizes and colors, processing and assembling circuits, designing circuit layouts, ordering electronic components from many reputable distributors. We can meet all the necessary needs of customers. Thank you for taking the time to read this article.
Some related articles:
FR4 – Material used in printed circuit boards
The reason why green is the main color in PCB production
Peeling of copper PAD during tin plating (HASL)
For more information, please contact:
Sales 01: 0965 833 553
Email 01: hatakeyvn@gmail.com
Sales 02: 0927 277 222
Email 02: sales.hatakeyvn@gmail.com
Service suggestions: 0971 687 227





 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt